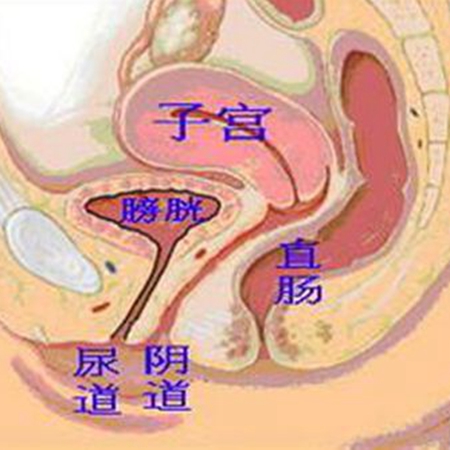
(1) Female internal reproductive organs: Female internal reproductive organs include vagina, uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes.
①Vagina: Between the bladder, urethra and rectum, it is a channel between the internal and external reproductive organs. It is the sexual organ and menstrual discharge channel of women, and it is also the only way for the fetus to be delivered during vaginal delivery. As a sexual organ, the outer 1/3 of the anterior vaginal wall is a sensitive area for sexual excitement.
②Uterus: The uterus is located in the true pelvic cavity, with the bladder in the front, adjacent to the rectum in the back, with ovaries, fallopian tubes and broad ligaments of the uterus on both sides, which are connected downward to the vagina. The uterus is the place where menstruation occurs, the passage for sperm to ascend during sex, and the place where the fetus grows after conception. It is shaped like an inverted pear and can be divided into two parts: the cervix and the uterus. When an adult woman is not pregnant, the uterus is about 7.5 cm long, 4 cm wide, and 2 to 5 cm thick.
③ Ovary: The ovary is the nest of eggs and the most important organ in the female reproductive organs. The ovaries are a pair of flat ellipsoids located on both sides of the uterus, which can periodically produce eggs and ovulation, and can secrete female hormones - estrogen and progesterone.
④ Fallopian tubes: The fallopian tubes are a pair of slender tubes located on the left and right sides of the uterus, about 10 cm long, one end is connected with the uterine horn, and the other end is free, close to the ovary. The top of the free end is umbrella-shaped and can pick up the eggs released by the ovary. The fallopian tube is the place where the sperm and egg combine to form a fertilized egg, and it is also the channel that transports the fertilized egg into the uterine cavity. When there are abnormal conditions such as inflammation of the fallopian tubes, the transportation of fertilized eggs will be affected, which is one of the important reasons for infertility or ectopic pregnancy (commonly known as ectopic pregnancy).
(2) Female external reproductive organs: female external reproductive organs include mons pubis, labia majora, clitoris, vaginal vestibule, and perineum.
Among them, the clitoris has erection and is a highly sensitive area for women.
① Mons pubis: It is located in the lowest part of the female anterior abdominal wall, that is, the fat pad that protrudes in front of the pubic symphysis. There is hypertrophic subcutaneous fat, and pubic hair begins to grow in this part of the skin during puberty, which is distributed in a downward-pointing triangle. Mons pubis has the function of protecting the genitals and preventing bacteria from invading the vagina.
② Labia majora: The labia majora is a pair of raised skin folds near the inner side. For unmarried or nulliparous women, the labia majora on both sides are naturally closed, covering the vagina and urethra, and the labia majora on both sides of multiparous women are often separated. The labia minora are a pair of thin folds located on the inside of the labia majora. The surface of the labia minora is moist like a mucous membrane, brown in color, with sebaceous glands, hairless, and rich in nerve endings, so it is extremely sensitive. When sexually excited, the labia minora are hyperemia and edema, which can increase by 2 to 3 times. It is one of the sexually sensitive areas.
③The clitoris: refers to the top between the labia minora on both sides. It consists of two erectile corpus cavernosums of different sizes. The clitoral head, rich in nerve endings, is extremely sensitive and erects when sexually excited. It is the most important part of the sexually sensitive organ.
④Vaginal vestibule: refers to the diamond-shaped area between the labia minora on both sides. The clitoris is above the vestibule, the urethral opening is in front of the vestibule, and the vaginal opening is behind it. The vaginal opening is covered by a thin mucous membrane called the hymen. There is a hole in the middle of the hymen. The size, shape, thickness and elasticity of the hole vary from person to person. Menstrual blood flows out of this hole. At the back of the labia majora is the Bartholin's gland, its duct opening in the groove between the labia minora and the hymen.
⑤ Perineum: refers to the soft tissue between the anus and the back of the labia.