As a woman, many people must not understand the appearance of their vulva. Therefore, I always feel that this is a private part, and I am embarrassed to observe it. In fact, knowing more about the structure of the vulva can better care for the vulva, because the female vulva is delicate and fragile, and needs special care. Some of them asked how the female vulva looks like? Don't worry, the editor will introduce you to the knowledge about the structure of the female vulva for your reference.
How many types of female vulva are there?
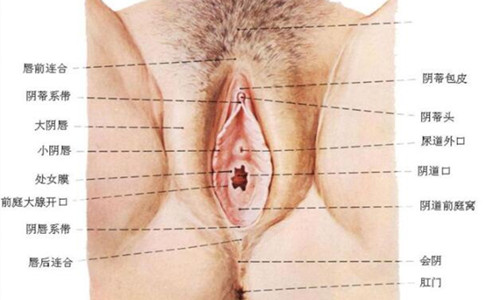
Female external genitalia refers to the exposed part of the reproductive organs, also known as the vulva. Generally speaking, it has two shapes, one is the full-bodied labia majora, and the lip shape is close to the bone; the other is the labia minora and labia majora both have long skin, some people say they are like butterflies ,Different lengths. In addition, the color of the female vulva is also divided into pink and brown. Generally, it is pink on the inside and brown on the outside. In general, they are bulging outward, and appear as two petals in the middle.
In addition, the female vulva is mainly composed of mons pubis, vestibular bulb, urethral opening, vestibule, vaginal opening, clitoris, labia minora, bartholin gland, and labia majora. The detailed information is as follows:
1. The mons pubis.
It is the raised part of the vulva in front of the pubic symphysis, composed of skin and a thick layer of fat. Pubic hair begins to grow on the skin during puberty and is distributed as a downward-pointing triangle.
2. Vestibular ball.
A pair of corpus cavernosums, also known as corpus cavernosum, are erectile. located on both sides of the vaginal opening. It is connected to the clitoral vein in the front, and the vestibular gland behind it. The surface is covered by the bulbocavernosus muscle, and it is easy to bleed after injury.
3. The urethra.
Between the lower border of the pubic symphysis and the vaginal opening, there is an irregular oval hole through which urine flows out. Its posterior wall has a pair of glands, called paraurethral glands, which open in the posterior wall of the urethra and are often where bacteria lurk. Therefore, the care of the female vulva must be paid attention to, otherwise it is easy to suffer from diseases.
4. The vestibule.
The prismatic area surrounded by the labia minora on both sides is called the vestibule. The surface is covered by mucous membranes, which is similar to a triangle. The tip of the triangle is the clitoris, the bottom is the labia frenulum, and the two sides are the labia minora. The opening of the urethra is in the upper vestibule. The vaginal opening is in its lower part, and in this area are the vestibular bulbs and the Bartholin glands.
5, vaginal opening.
The vaginal opening is covered by an incompletely closed mucous membrane called the hymen. There is a hole in the middle of the hymen from which menstrual blood flows. The size of the hymen hole and the thickness of the membrane vary from person to person. After the hymen is ruptured, the mucous membranes appear as many small spherical objects, which become hymen scars.
6. The clitoris.
Located at the top between the labia minora on both sides, it is a small oblong organ with a round head at the end, and the inner end is connected with a thin bundle of erectile tissue. Erectile tissue is a kind of cavernous tissue, rich in venous plexus and rich in nerve endings, so it feels sharp and easy to bleed after injury. A woman's clitoris is equivalent to the glans of a man's penis.
7. The labia minora.
It is a pair of mucosal folds, which are moist on the inner side of the labia majora. The upper bifurcations of the left and right sides of the labia minora join with each other, the upper skinfold is called the clitoral foreskin, the lower skinfold is called the clitoral frenulum, and the clitoris is in the middle of them. The lower ends of the labia minora meet under the vaginal opening and are called the labia frenulum. There are abundant nerve distribution under the mucosa of labia minora, so the feeling is sensitive.
8. The Bartholin's gland is also called the Bartholin's gland.
Located at the lower end of the vagina, behind the labia majora, it is also covered by the bulbocavernosus muscle. It is a gland the size of a small broad bean on one side. Its glandular duct is very narrow, about 1.5 to 2 cm, and opens on the inner side of the lower end of the labia minora. The epidermis of the glandular duct is mostly squamous epithelium, and only the innermost end of the tube is composed of a layer of columnar cells. When sexually excited, it secretes yellow-white mucus to lubricate the vaginal opening. This gland cannot be touched during normal examination.
9. The labia majora.
It is a pair of oblong raised skin folds on both sides of the vulva, near the inner sides of the two strands. The front is connected to the mons pubis, and the back is connected to the perineum; it starts from the mons pubis and stretches downward and backward. The left and right labia majora in front combine to become the front combination, and the two ends at the back combine to form the rear combination. The rear combination is located in front of the anus, but not as good as the front combination. obvious. Pubic hair grows on the outside of the labia majora. Subcutaneous adipose tissue, elastic fibers and venous plexus are prone to hematoma after injury.
Among them, the labia majora of unmarried women are naturally closed to cover the vaginal opening and urethral opening. The labia majora of a multiparous woman are separated on both sides due to the effects of childbirth.
The above has introduced the structure of the female vulva, and you must have some knowledge about the vulva. The editor reminds women to take more care of the vulva in their daily life. once they find itching, redness, pain and other problems in the vulva, they must go to the hospital for examination in time, so as not to delay the treatment of the disease.