导读:据一份权威报告称,如果全世界不立刻采取行动,到2050年时全球每3秒钟就会有一人死于超级病毒。
The global review sets out a plan for preventing medicine "being cast back into the dark ages" that requires billions of dollars of investment.
为防止现代医药“被抛回黑暗时代”,这份全球调查提出了一份计划,需要数十亿美元的投资。
It also calls for a revolution in the way antibiotics are used and a massive campaign to educate people.
这份计划还呼吁变革目前抗生素的使用方法,并开展大规模的运动来教育民众。
The report has received a mixed response with some concerned that it does not go far enough.
对于这份报告,人们的评价有褒有贬。也有人提出,这份报告对于问题的严重性还不够深入。
The battle against infections that are resistant to drugs is one the world is losing rapidly and has been described as "as big a risk as terrorism".
在这场和耐药性感染病的战斗中,人类正在快速的失败,外界将其描述为“和恐怖主义一样的巨大风险”。
The problem is that we are simply not developing enough new antibiotics and we are wasting the ones we have.
现在的问题是,我们没有开发出足够的新抗生素,而且我们正在浪费我们已经拥有的一些抗生素。
Since the Review on Antimicrobial Resistance started in mid-2014, more than one million people have died from such infections.
自从2014年年中开始这场抗菌素耐药性调查以来,已经有超过一百万人死于这些抗药性感染病。
And in that time doctors also discovered bacteria that can shrug off the drug of last resort - colistin - leading to warnings that the world was teetering on the cusp of a "post-antibiotic era".
在这次调查期间,医学专家们还发现细菌可以依靠“粘菌素”来摆脱药物的影响,从而警告说全世界正处于一个“后抗生素时代”的风口浪尖上。
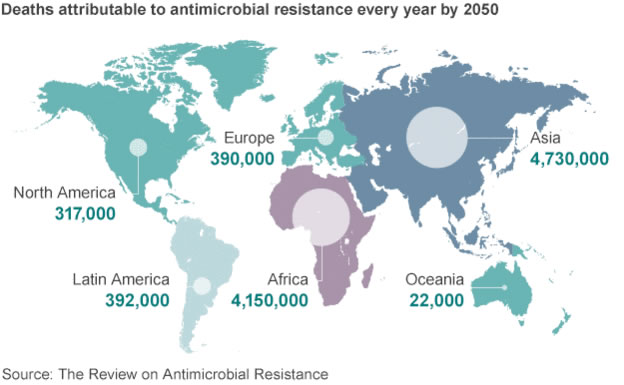
The review says the situation will get only worse with 10 million people predicted to die every year from resistant infections by 2050.
据调查结果显示,目前的局势将会持续恶化,预计到2050年时每年将会有1000万人死于耐药性感染病。
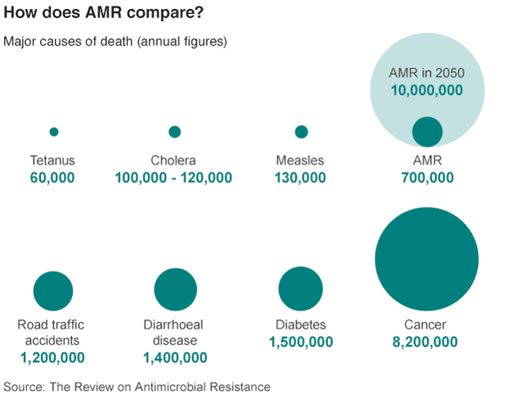
And the financial cost to economies of drug resistance will add up to $100 trillion (?70 trillion) by the mid-point of the century.
而到本世纪中叶,用于药物抗性经济的成本将达到100万亿美元(约合70亿英镑)。
The review said the economic case for action "was clear" and could be paid for using a small cut of the current health budgets of countries or through extra taxes on pharmaceutical companies not investing in antibiotic research.
据这份调查表示,相关的经济应对措施“很明确”,国家可以略微减少一点医疗卫生方面的预算,或者对不投资抗生素研发的制药企业征收额外的税收。
Lord Jim O’Neill, the economist who led the global review, told the BBC: "We need to inform in different ways, all over the world, why it’s crucial we stop treating our antibiotics like sweets.
诺德·吉姆·奥尼尔是主持这份全球调查的经济学家,他告诉BBS说:“我们需要通过不同的渠道来告诉全世界,为什么过去深受我们喜爱的抗生素是‘毒药’而不是糖果。”
"If we don’t solve the problem we are heading to the dark ages, we will have a lot of people dying.
“如果我们现在不解决这个问题,那么我们就将进入黑暗时代,许多人将死去。”
"We have made some pretty challenging recommendations which require everybody to get out of the comfort zone, because if we don’t then we aren’t going to be able to solve this problem."
“我们提供了一些很有挑战性的建议,这些建议要求所有人必须离开安全区。因为如果我们不这样做的话,我们就将不可能解决这个问题。”







